Image Source: Google
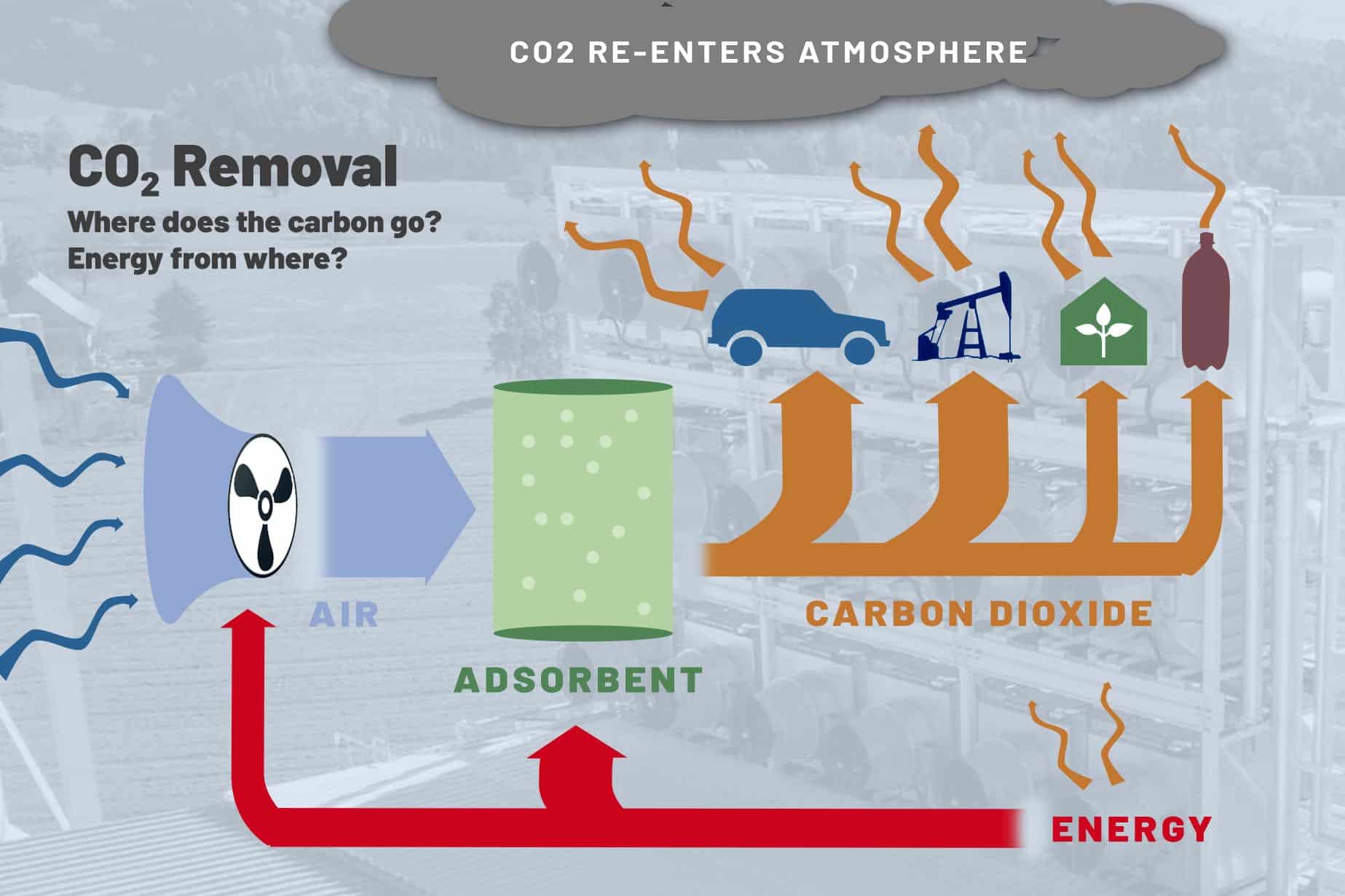
One of the most pressing issues facing our planet today is the increasing levels of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere and its impact on climate change. As we continue to burn fossil fuels and clear forests at an alarming rate, the concentration of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere has reached levels not seen in millions of years. To combat this growing crisis, scientists and engineers have been working tirelessly to develop new technologies to remove carbon dioxide from the air and store it safely. One such technology that shows great promise is atmospheric carbon capture. Refer: https://svanteinc.com/carbon-capture-solutions/.
Atmospheric carbon capture is a process by which carbon dioxide is removed from the air and stored in a way that prevents it from re-entering the atmosphere. There are several different methods for achieving this, including direct air capture, bioenergy with carbon capture and storage (BECCS), and afforestation. Each of these methods has its strengths and weaknesses, but all have the potential to play a key role in helping to reduce the level of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere and mitigate the impacts of climate change.
One of the main advantages of atmospheric carbon capture is its scalability. Unlike some other forms of carbon capture, such as capturing emissions from industrial sources, atmospheric carbon capture can be deployed anywhere in the world. This means that it has the potential to make a significant impact on a global scale, helping to reduce carbon dioxide levels no matter where they originate. Additionally, atmospheric carbon capture can be used in conjunction with other forms of carbon reduction, such as renewable energy sources and energy efficiency measures, to further reduce greenhouse gas emissions and combat climate change.
Another key benefit of atmospheric carbon capture is its potential to create new economic opportunities. As the technology continues to develop and become more widespread, there will be a growing need for skilled workers to design, build, and operate carbon capture facilities. This could create thousands of new jobs in the clean energy sector, helping to boost local economies and reduce unemployment. Additionally, the captured carbon dioxide can be used in a variety of ways, such as in the production of fuels, chemicals, and building materials, creating new revenue streams, and driving innovation in a wide range of industries.
While atmospheric carbon capture holds great promise for the future of sustainability, there are still some challenges that need to be overcome for it to reach its full potential. One of the main challenges is the cost of capturing and storing carbon dioxide. While the cost of carbon capture technologies has been decreasing in recent years, it is still relatively expensive compared to other forms of carbon reduction. This is why governments and businesses must invest in research and development to drive down costs and make atmospheric carbon capture more affordable and accessible.
Another challenge is the issue of public acceptance. While most people agree that something needs to be done to reduce carbon dioxide levels in the atmosphere, there is still some skepticism around the idea of capturing carbon dioxide directly from the air. Some worry that the technology could have unintended consequences or that it could be used as an excuse to continue burning fossil fuels. It will be important for scientists, engineers, and policymakers to engage with the public and address these concerns to build trust and support for atmospheric carbon capture.
Despite these challenges, the future of sustainability with atmospheric carbon capture looks bright. As the technology continues to improve and costs come down, we will be able to deploy atmospheric carbon capture on a much larger scale, helping to significantly reduce carbon dioxide levels in the atmosphere and combat climate change. By investing in research and development, creating new economic opportunities, and building public support, we can unlock the full potential of atmospheric carbon capture and create a more sustainable future for generations to come.

